PERSPECTIVE ANALYTICS ™
Perspective Analytics
What is Perspective Analytics?
“Perspective analytics is a process that helps marketers move from start to scale by targeting actionable insights v. more traditional, linear data analysis/response approaches.”
Perspective Analytics represents an advanced methodology within the realm of marketing analytics, distinguished by its dynamic and multifaceted approach. This strategy transcends the conventional bounds of straightforward data monitoring and linear analysis techniques. Unlike traditional methods that often focus solely on data collection and basic interpretation, Perspective Analytics is designed to delve deeper into the data to unearth significant, actionable insights that can directly influence business strategies and outcomes.
At its core, Perspective Analytics aims to enhance the decision-making process by integrating various data points to provide a holistic view of the customer journey. It prioritizes the creation of value for both the business and its customers. By analyzing interactions, behaviors, and patterns from multiple perspectives, this approach helps identify unique opportunities for enhancing visitor or customer experiences and offers tailored, impactful solutions that address specific needs and preferences.
Furthermore, Perspective Analytics employs innovative tools and technologies to dynamically adapt to changing market conditions and consumer trends. This adaptive capability ensures that businesses remain agile, responsive, and competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace. Through the strategic use of Perspective Analytics, organizations can achieve a more profound understanding of their audience, optimize their marketing efforts, and drive meaningful engagement and growth.
Perspective Analytic: Stages and Approach
Information
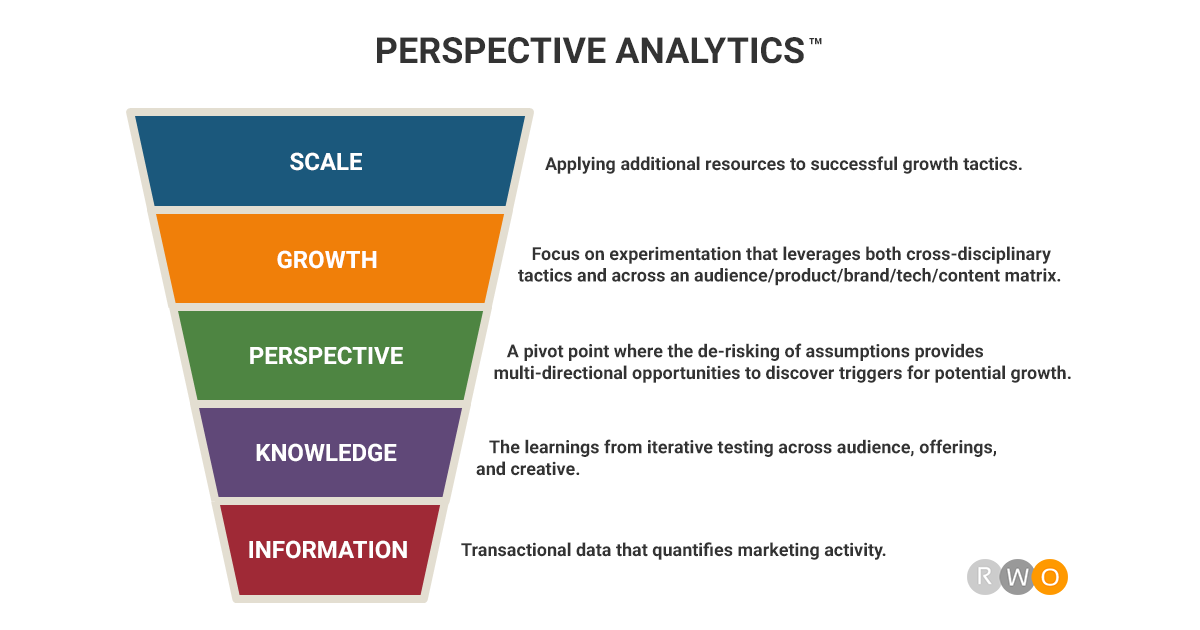
The development stages of perspective analytics include: information, knowledge, perspective, growth, and scale.
The Information stage is foundational to Perspective Analytics. In traditional approaches, marketers often stop at collecting and quantifying transactional data. Here, however, this stage serves as a base camp for a much higher climb. It includes gathering and synthesizing a wide variety of data, from user behavior and engagement metrics to sales data and customer feedback. By doing so, you create a comprehensive landscape of information that goes far beyond mere numbers.
Moreover, the Information stage also involves advanced analytics techniques such as sentiment analysis, churn prediction, and customer segmentation. This allows marketers to delve deeper into the “why” behind the “what,” thereby empowering them to anticipate market trends and customer behavior more effectively. This holistic approach sets the stage for more insightful and strategic actions in the subsequent stages of Perspective Analytics.
Knowledge
After collecting a diverse set of information, the Knowledge stage is about turning this raw data into actionable insights. The information gathered isn’t just collated but is tested iteratively across different audience segments, product offerings, and creative content. These iterative tests allow for hypothesis-driven experiments that can result in more than just incremental improvements; they can sometimes lead to breakthrough innovations.
More importantly, this stage includes the application of machine learning algorithms and other advanced analytical tools to identify less obvious patterns and correlations. By employing a multi-disciplinary approach, this stage leads to the creation of a knowledge hub that is not just descriptive but predictive and prescriptive, informing not only what is happening but also what is likely to happen and what actions should be taken.
Perspective
Perspective is the pivot point in this analytical approach. Unlike traditional analytics that operate in a linear fashion, Perspective introduces multi-dimensionality. This involves de-risking assumptions and using the acquired knowledge to view data from multiple angles. It’s not just about understanding what has succeeded or failed but also gaining a nuanced understanding of the factors that led to those outcomes.
This stage allows for more adaptive and dynamic strategies by identifying triggers and levers for growth that may be less apparent. It encourages an exploratory mindset, pushing marketers to question existing assumptions and explore unfamiliar avenues. The ultimate aim is to unlock new opportunities for growth by developing a more holistic view of the business landscape.
Growth
The Growth stage is where the rubber meets the road. Having acquired a multi-faceted perspective, it’s time to apply it through targeted experimentation. These experiments aren’t just limited to traditional marketing avenues but span a matrix that includes audience, product, brand, technology, and content. Each experiment is designed to test specific hypotheses, drawn from the insights gained in the earlier stages.
Moreover, this stage involves not just single, isolated experiments but often multi-variate tests that are designed to measure the impact of various factors simultaneously. The focus is on rapid iteration, quick learning, and agile implementation. Successful tactics are then optimized and scaled, while less effective ones are either refined for re-testing or discarded, all with the aim of discovering stepped improvements in performance and yield.
Scale
Scaling is the ultimate objective, but it only occurs when there is a consistent upward trajectory in growth results. This stage involves allocating more resources, whether it’s budget, manpower, or technological assets, to strategies and tactics that have shown promise. But scaling isn’t just about increasing the volume; it’s about optimizing performance at every level to ensure that growth is sustainable over the long term.
This also involves continuous monitoring and feedback loops, to ensure that scaling efforts are aligned with actual performance and market conditions. It’s about creating a virtuous cycle where the insights gained from scaling feed back into the information stage, thereby continuously refining and enhancing the Perspective Analytics process.
Additional Principles to Perspective Analytics
-
- Focus on value-adds for the visitor/customer
Focusing on value-adds is all about enhancing the customer experience. The key here is to go beyond the rudimentary offerings and provide something that genuinely enriches the visitor’s interaction with your brand. This could be as simple as a well-designed UI/UX, or as complex as personalized recommendations based on user behavior. The idea is to make each touchpoint meaningful, thereby creating loyal customers who not only make a purchase but become advocates for your brand.
This focus requires a nuanced understanding of your customers’ needs, pain points, and aspirations. Through data analytics and customer insights, tailor your offerings to address these specific aspects. By focusing on value, you’re not just selling a product or service; you’re establishing a relationship and building a community around your brand.
-
- Learn quickly what works and discard what doesn’t
The world of analytics is often a fast-paced environment where the ability to adapt is key. Learning quickly what works allows organizations to efficiently allocate resources towards strategies and tactics that yield results. This is not just about celebrating successes but involves rigorous A/B testing, control groups, and real-time feedback to validate what’s working.
On the flip side, it’s equally important to identify what’s not working and make informed decisions to either pivot or discard these elements. This saves not just money but also time, enabling the organization to focus on actionable insights that contribute to measurable outcomes.
-
- De-risk assumptions across the sales funnel
Assumptions are often the invisible pitfalls in any analytics approach. By de-risking assumptions across the sales funnel, you ensure that each stage is optimized for maximum efficiency and effectiveness. This involves questioning traditional wisdom and established norms, from lead generation to customer retention. This isn’t about eliminating risks entirely but about managing them in a way that they don’t become roadblocks.
De-risking involves a mix of data-driven insights and predictive analytics. By simulating different scenarios and outcomes, you can anticipate potential challenges and preemptively develop solutions. This creates a more resilient and adaptable sales funnel that is robust against unforeseen variables.
-
- Create adaptive responses to external parameters (pivot) within a lean marketing system
Markets are dynamic, and a static analytics approach is a recipe for obsolescence. Creating adaptive responses means developing systems that can quickly pivot in response to external changes, whether those are market trends, customer behavior, or even global events. The agility to pivot is not just a tactical advantage; it’s a strategic imperative.
In a lean marketing system, resources are already optimized for efficiency. Adding adaptive responses to this system means you’re not just doing more with less, but you’re doing it smarter. This involves real-time data tracking and automated decision-making systems that can adjust marketing strategies in an agile manner.
-
- Help establish a culture of systemic creativity and innovation
Analytics shouldn’t be a siloed function, detached from the creative and innovative aspects of your organization. A culture of systemic creativity and innovation means embedding analytics into every process and decision-making framework. This synergy between analytics and creativity fosters an environment where data informs creativity and vice versa.
Such a culture is not established overnight. It requires leadership commitment, ongoing training, and a rewards system that incentivizes innovative thinking. Over time, this culture not only produces better analytics results but also drives the entire organization towards a path of continuous improvement and sustainable growth.
Perspective Analytics
What is Perspective Analytics?
Perspective Analytics Approach
Information
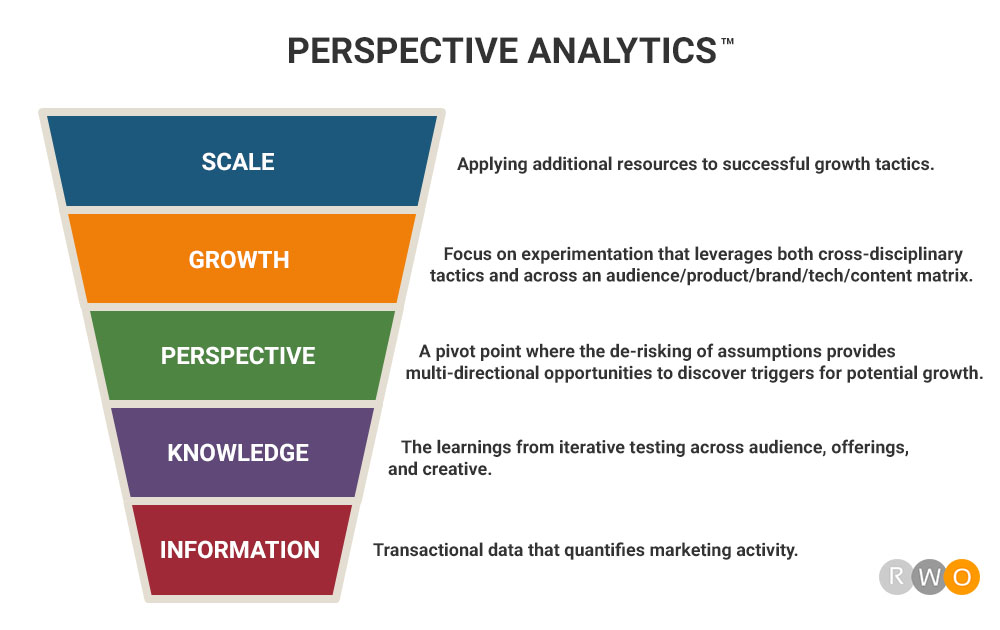
The information stage is where many marketers begin and sometimes end their analytics journey with transactional data that quantifies marketing activity.
Knowledge
Knowledge includes facts, information, and even skills acquired through the learnings from iterative testing across audience, offerings, and creative.
Perspective
This literal “point of view” is a pivot point where the de-risking of assumptions provides multi-directional opportunities to discover triggers for potential growth.
Growth
This stage of growth focuses on experimentation that leverages both cross-disciplinary tactics and across an audience, product, brand, tech, and a content matrix of potential opportunities for discovery of stepped improvements in yields.
Scale
As long as the growth results trajectory is moving in the upward direction, it is now the time to apply additional resources to these successful growth tactics.
Additional Principles to Perspective Analytics
- Focus on value-adds for the visitor/customer
- Learn quickly what works and discard what doesn’t
- De-risk assumptions across the sales funnel
- Create adaptive responses to external parameters (pivot) within a lean marketing system
- Help establish a culture of systemic creativity and innovation
